# Configure SQL Server as your data pipeline destination
Set up SQL Server as a destination for your data pipeline. This connection enables Workato to replicate data from source applications into your SQL Server instance using the source schema.
# Features supported
The following features are supported when using SQL Server as a pipeline destination:
- Automatic creation of destination tables based on source schema
- Support for full and incremental data loads
- Field-level data replication without explicit field mapping
- Schema drift handling and update operations
# Prerequisites
You must have the following configuration and access:
- A SQL Server instance reachable from Workato (Cloud or On-prem group)
- A user with privileges to create tables and write data
- Host, port, database, and authentication credentials
SQL Server OPA requirement
Workato requires SQL Server OPA version 29.1 or above to support data pipelines.
# Connect to SQL Server
Complete the following steps to connect to SQL Server as a data pipeline destination. This connection allows the pipeline to write records into a target table in your SQL Server instance.
Connect to SQL Server
Select Create > Connection.
Search for and select SQL Server on the New connection page.
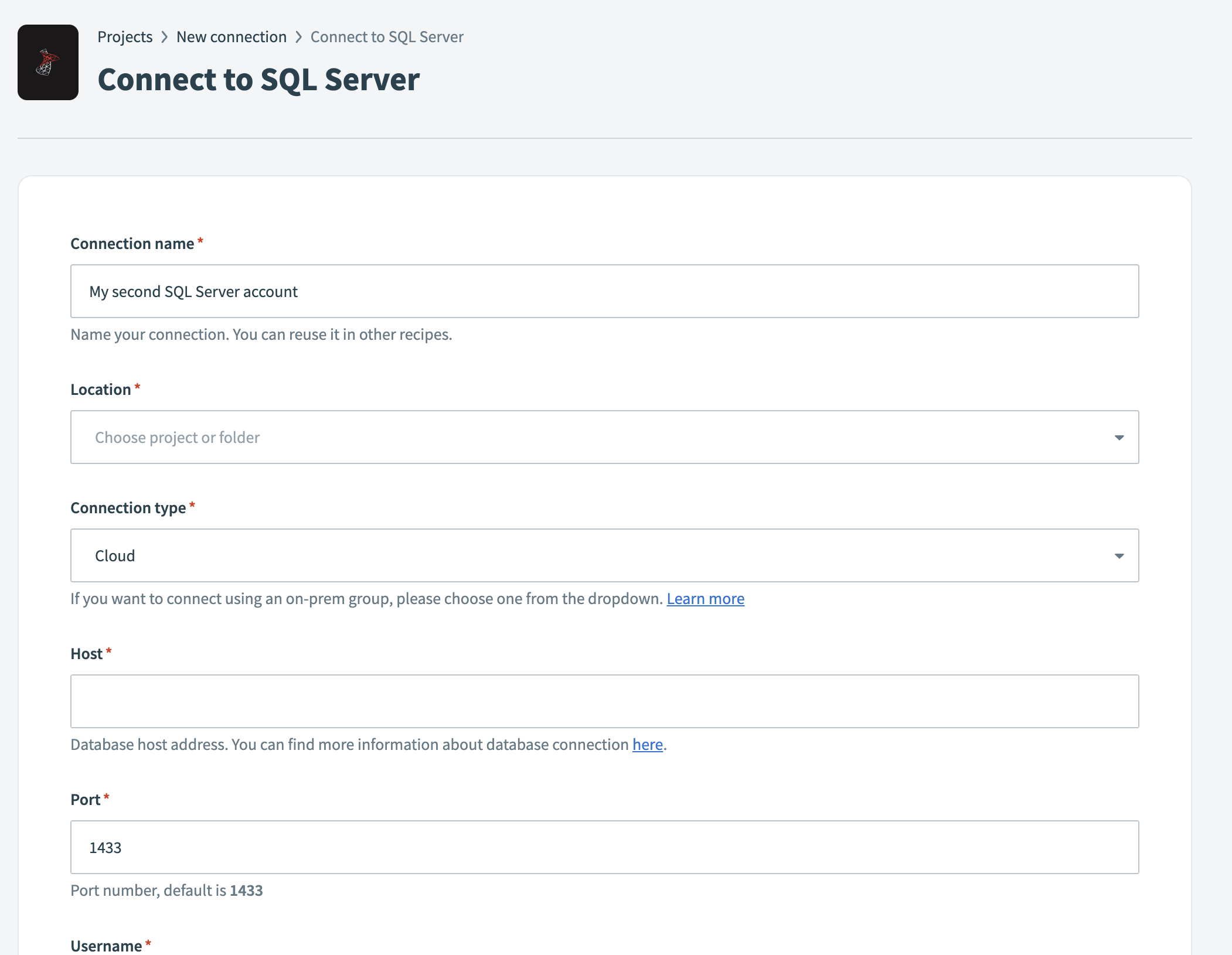
Enter a name in the Connection name field.
 SQL Server connection setup
SQL Server connection setup
Use the Location drop-down to select the project where you plan to store the connection.
Select Cloud in the Connection type field, unless you need to connect through an on-prem group.
Enter the URL of your hosted server in the Host field.
Enter the port number your server runs on in the Port field. The default port for SQL Server is 1433.
Enter the username to connect to SQL Server in the Username field.
Enter the password to connect to SQL Server in the Password field.
Enter the name of the SQL Server database you plan to connect to in the Database field.
Optional. Specify whether you're connecting to an Azure SQL instance in the Azure SQL field. The default is No.
Optional. Expand the Advanced settings field to configure additional settings:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Use improved datetime handling | Enable enhanced handling of datetime, datetime2, and datetimeoffset datatypes in SQL Server. Defaults to true. Refer to the Improved datetime handling section for more information. |
| Database timezone | Set your database's local timezone. When timezones are provided for datetime and datetime2 datatypes, values convert to this timezone before insertion. Default is UTC. |
Select Connect to verify and store the connection.
# Configure the destination action
Before you start the pipeline, ensure the schema in SQL Server is newly created and empty. This prevents errors during the initial sync and allows the pipeline to create destination tables without conflicts.
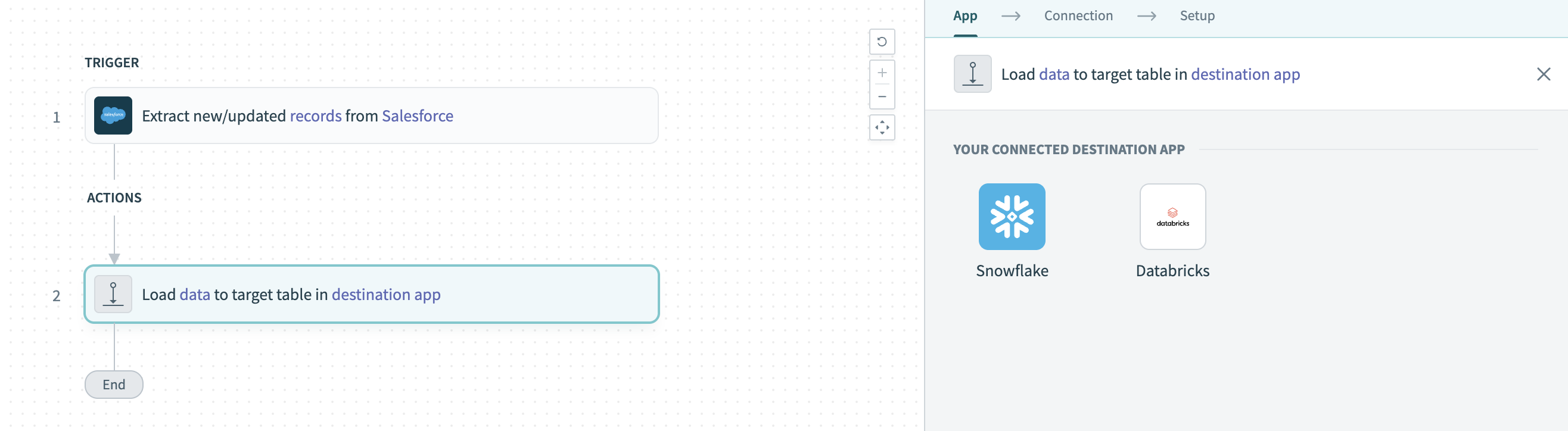
Click the Load data to target table in destination app action. This action defines how the pipeline replicates data in the destination.
 Configure the Load data to target table in destination app action
Configure the Load data to target table in destination app action
Select SQL Server in the Your Connected Destination App field.
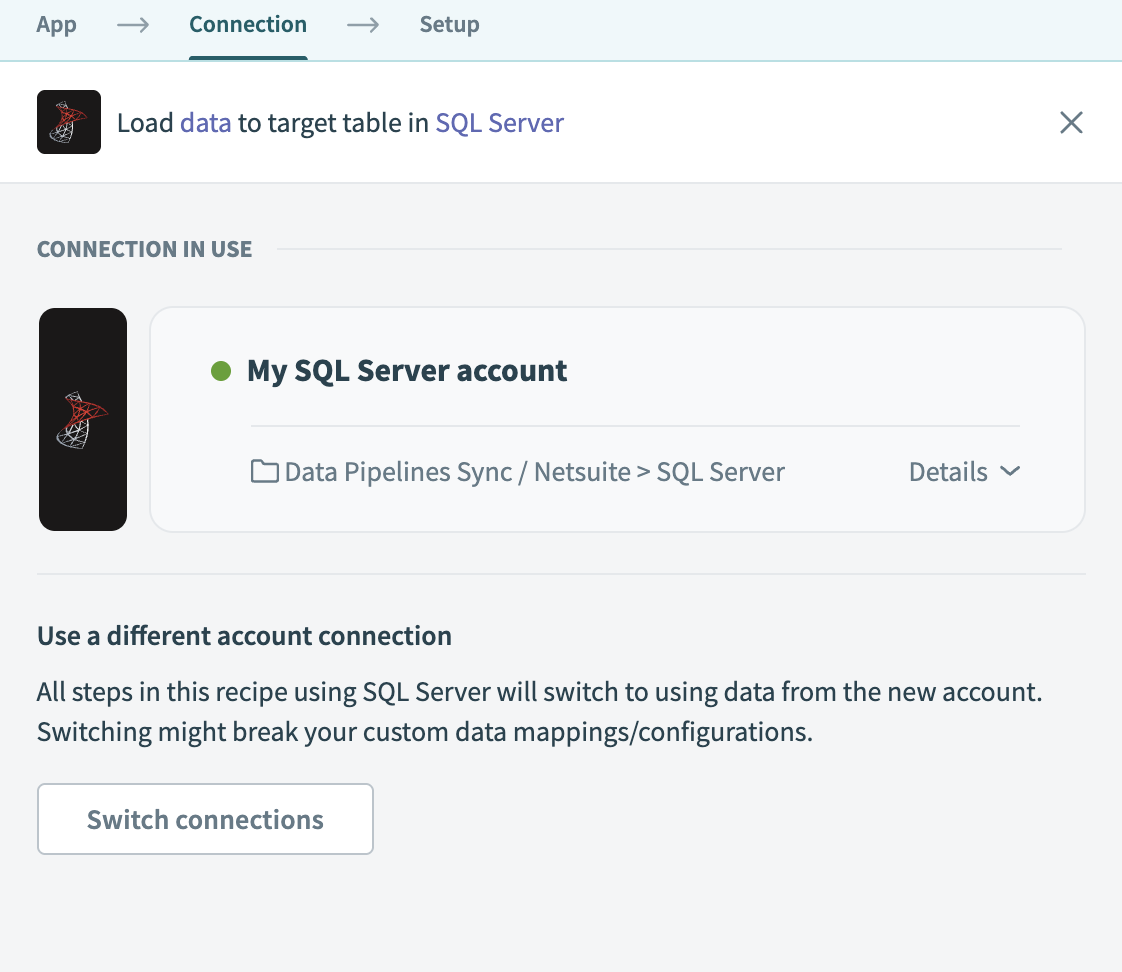
Choose the SQL Server connection you plan to use for this pipeline. Alternatively, click + New connection to create a new connection.
 Choose a SQL Server connection
Choose a SQL Server connection
The Load data to target table in destination app action automatically replicates the object schema from the source to SQL Server. Explicit field mapping isn't required.
Workato pipelines automatically create destination tables based on the source schema. The pipeline also creates a stage and temporary tables to support data replication and update operations.
Select Save to save the pipeline.
# Identifier handling
SQL Server treats unquoted identifiers as case-insensitive and stores them in uppercase by default. Workato pipelines translate source column names into valid SQL Server identifiers by applying the following rules:
- Column names are uppercased
- Special characters such as
$, spaces, or dashes are replaced with underscores (_) - Identifiers are wrapped in square brackets to support special characters and reserved words
This ensures compatibility with SQL Server table creation and querying behavior.
# Example
The following source table structure:
| Source object | Source field |
|---|---|
Account | $Name$, Created Date, Limit |
Results in the following table created in SQL Server:
CREATE TABLE [ACCOUNT] ([_NAME_], [CREATED_DATE], [LIMIT])
Unquoted queries can reference columns without case sensitivity:
SELECT created_date FROM account;
Bracketed queries must match the exact identifier format:
SELECT [_NAME_] FROM [ACCOUNT];
Last updated: 2/6/2026, 5:48:07 PM